Complete Guide to AI Marketing in 2026: Strategies, Tools & ROI
Discover the future of AI marketing with a deep dive into the top AI tools of 2026, proven strategies, and a systematic process to implement AI across your marketing efforts.

AI marketing is not a passing trend. The market is on track to hit USD 217.33 billion by 2034, and spending is already following results.
Roughly three out of four marketers now use AI in some form. Yet only about a third can point to results they truly trust, revenue they can defend in a meeting, time savings that actually changed how their team works, or performance gains that didn’t vanish after a quarter.
That gap didn’t happen because the tools are bad. It happened because many teams rushed in without a plan, expected instant wins, or treated AI like a magic switch instead of a system that needs care.
A few years ago, AI meant auto-generated copy and basic chatbots. Helpful, but limited. Fast forward to 2026 and things look very different. AI now predicts buying behavior, helping in targeted audience segmentation, reshuffles ad budgets mid-campaign, adjusts emails based on individual reading habits, and spots churn risks before customers complain.
This guide is for people who want AI to pull its weight.
You’ll learn how AI marketing actually shows up in real teams today, which use cases are worth your time, which tools earn their cost, and how to measure results without fooling yourself.
The State of AI Marketing in 2026
Here are some really amazing counts and fact on related to AI usage in marketing:
According to Gartner, by 2026, nearly 60% of CMOs will adopt safeguards to protect their brands from generative AI–driven deception.
According to the source, AI in the marketing domain can significantly enhance productivity by up to 47%, mainly by reducing low-value and manual tasks.
In its recent research, Statista found that the global market revenue from AI usage in marketing will reach USD 107 billion by 2028.
Key trends shaping AI marketing:
Generative AI Maturation: Using generative AI has become a regular part of many marketing activities. When looking at how generative AI is being used today, it is less about experimentation with generative AI tools and more about understanding how this technology can best benefit and where it should be limited, and what roles need to be performed by people.
Predictive Analytics Mainstream: Predictive analytics have become standard operating procedures for almost all marketing plans. It has turned into the core aspect while preceding decision-making processes. The project management team members can take comfort in knowing that predictive analytics can offer guidance and not a 100% guarantee of anything.
Hyper-Personalization at Scale: Hyper-personalization is now a dynamic process that's happening across all marketing channels rather than looking at fixed segments, it is based on the actual customer behaviours. The result of doing this correctly makes customers/users feel personal, relevant and engaging. However, hyper-personalization can also be taken too far, which causes the customer to feel a sense of intrusion, and customers notice.
AI-Powered Customer Service: Most routine customer inquiries are now being handled by artificial intelligence (AI), in many cases without the customer realizing it. This allows human agents to concentrate on more complicated inquiries that require an understanding of customer judgement, empathy, and provide a meaningful experience.
Autonomous Campaign Optimization: Campaigns can now change their budgets, bids, and creative elements in a matter of seconds with very little input from the marketer. The marketer now has more time to analyse results, test ideas and make necessary adjustments when things are off course.
AI Marketing Categories: An Overview
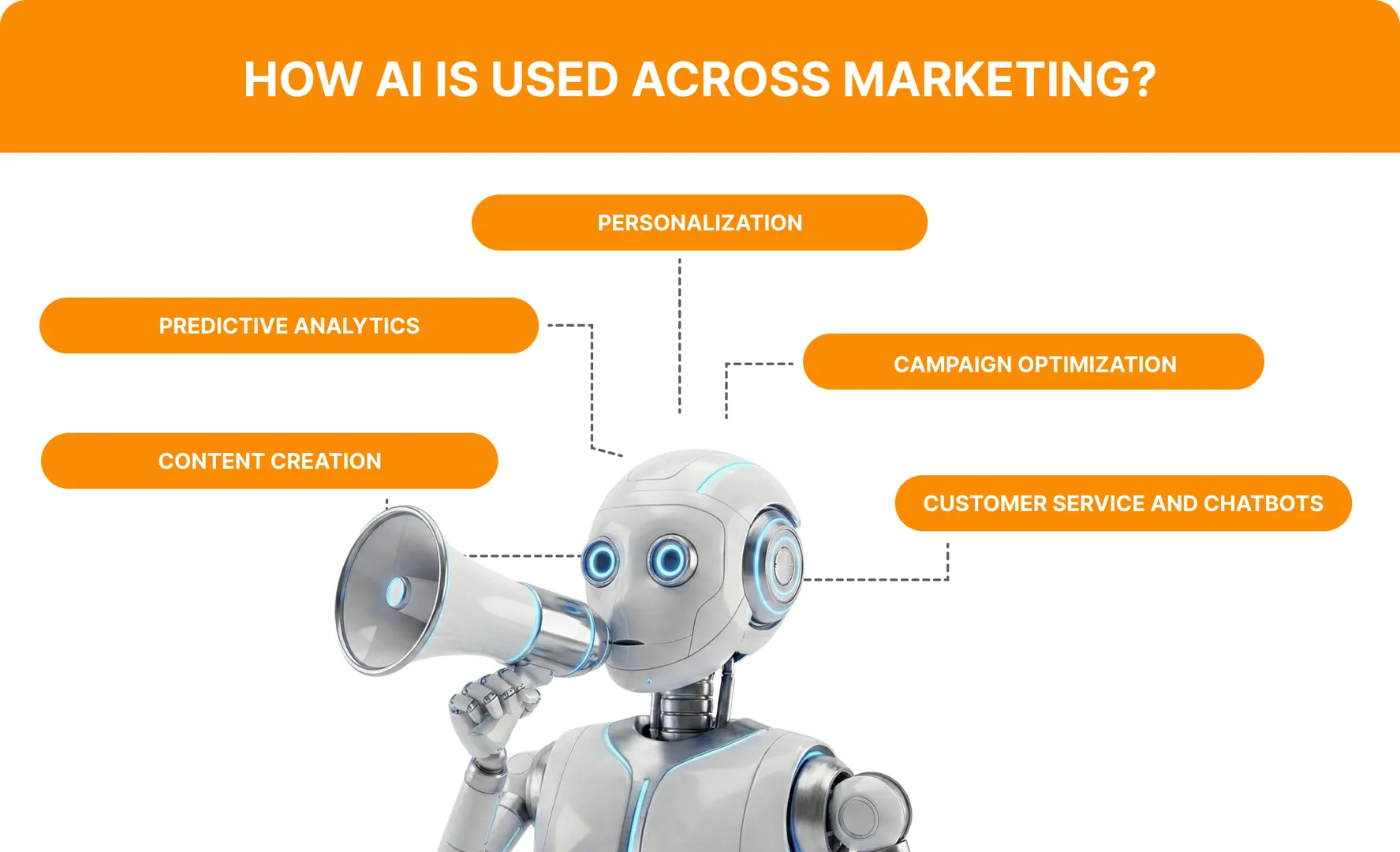
Content Creation
AI now helps with the entire content cycle. Brainstorming, drafts, rewrites, testing headlines, resizing visuals, and turning one idea into ten formats.
Good teams don’t let AI publish unchecked. They use it as a fast first pass. The human touch still matters. Voice, judgment, and taste don’t come from a prompt. The payoff is speed. What once took a week now takes a morning.
Predictive Analytics
This is where AI starts paying for itself. Instead of guessing who might buy or leave, teams use AI to spot patterns early. Who’s likely to churn. Which leads will close. Which customers will spend more over time.
Retail teams use this to plan promotions. SaaS teams use it to protect renewals. E-commerce teams use it to decide who deserves a discount and who doesn’t.
Personalization
Personalization used to mean “Hi {First Name}.” Now it means emails that change based on reading habits, product pages that reorder themselves, and recommendations that feel oddly accurate.
Most teams don’t build this from scratch. They use AI systems that react to behavior in real time, without dozens of brittle rules.
Campaign Optimization
Paid media has changed more than most people admit. AI now controls bidding, placement, creative rotation, and budget shifts. Human teams set direction and boundaries. Machines handle the constant adjustments. When this works well, waste drops fast. When it’s poorly set up, money disappears just as quickly.
Customer Service and Chatbots
Chatbots grew up. They read tone. They know when to escalate. They spot frustration before tickets pile up. Some even follow up after an issue is resolved.
Support teams use them to handle volume. Marketing teams use the data to understand what customers complain about most.
Core AI Tools Powering Modern Marketing
AI marketing without the right tools and platforms isn’t even imaginable. AI starts delivering results only when it’s integrated smartly and used with a clear purpose. So here’s a quick list of tools that you, as a marketing professional, should focus on or prioritize in your workflow.
Content Creation
Writing is still human work. AI just helps you get unstuck and move faster.
ChatGPT / Claude
Drafting rough copy, reshaping messy thoughts, or testing different tones before committing. You don’t publish straight from them but they save hours. curious how ChatGPT will rule the future? Check out the latest ChatGPT Trends.Jasper
Blogs, nurture emails, landing pages, Jasper keeps things consistent when multiple people are writing at once.Copy.ai
Short, sharp copy is its sweet spot. Ads, headlines, CTAs. You run a few options, tweak the best one, and move on.Canva AI
Perfect for moments when you need something decent now. Social graphics, decks, quick visuals, no waiting on design queues.
Email Marketing
Email works best when it feels more timely and personalized but less automated.
Klaviyo AI
Strong for brands that sell products. It predicts who’s likely to buy, churn, or ignore you and adjusts campaigns based on that.ActiveCampaign
Built for behavior-based flows. When someone clicks, downloads, or goes quiet the system reacts without manual effort.Seventh Sense
Simple idea, real impact. It figures out when each person actually opens emails and sends accordingly.
If revenue matters most, Klaviyo usually wins. If journeys matter, ActiveCampaign. If openings are lagging, Seventh Sense earns its place.
Social Media
Posting on social media platforms is getting easier, faster, and more seamless than ever. AI marketing tools are backed us including:
Buffer AI Assistant
Helps clean up captions, shape ideas, and keep posting consistent without overthinking every line.Hootsuite Insights
This is where listening happens. You see what people are saying, how sentiment shifts, and which topics won’t die.Lately.ai
Great when long-form content is already there. One blog turns into dozens of social posts without rewriting everything.
SEO & Content Optimization
The way SEO is growing, its AI tools need to be explored soon and used with immediate effect. Manual SEO activities need time, effort, consistent eye, and more. With AI-powered SEO tools now care less about keywords alone and more about coverage.
Surfer SEO
This is the tool teams use when a page isn’t ranking and they want clear direction. It points out gaps structure, headings, word count, terms competitors already cover.Clearscope
Writers use it to check whether a piece feels complete, not thin. It’s less about fixing pages and more about writing stronger ones from the start.MarketMuse
Best when content is a long-term play. It shows gaps across topics, not just pages.Frase
Strong for early research and pulls SERP patterns into one place so writers don’t start blind.
Analytics & Reporting
Analytics tools matter when they answer questions faster than meetings do. Insight- and decision-driven direction, instead of blind marketing, can completely transform how analytics and reporting shape the execution of marketing activities.
Google Analytics 4
Spots trends and odd behavior quickly. Useful when traffic changes and no one knows why.HubSpot Predictive Analytics
Ties marketing activity to leads and deals. Helpful when marketing and sales finally sit at the same table.Tableau Einstein
Built for teams swimming in data. Strong visuals, deeper forecasts, heavier setup.
Advertising
Advertising is where AI quietly makes the biggest difference mostly by reacting faster than humans can do, optimization, and result driven way.
Google Performance Max
It handles placements, bidding, and formats across Google’s inventory. Less control, but often better reach and efficiency.Meta Advantage+
It tests audiences and creatives continuously, making it useful for brands running frequent campaigns or promotions.Albert.ai
Suited for brands running campaigns across many channels without hands-on control every day.
AI Marketing Implementation Framework
AI implementation in marketing is not as easy as it seems. It requires unbeatable planning, disciplined execution, and continuous outcome measurement. Here, we’ve outlined a structured approach to help you implement AI marketing through clearly defined phases.
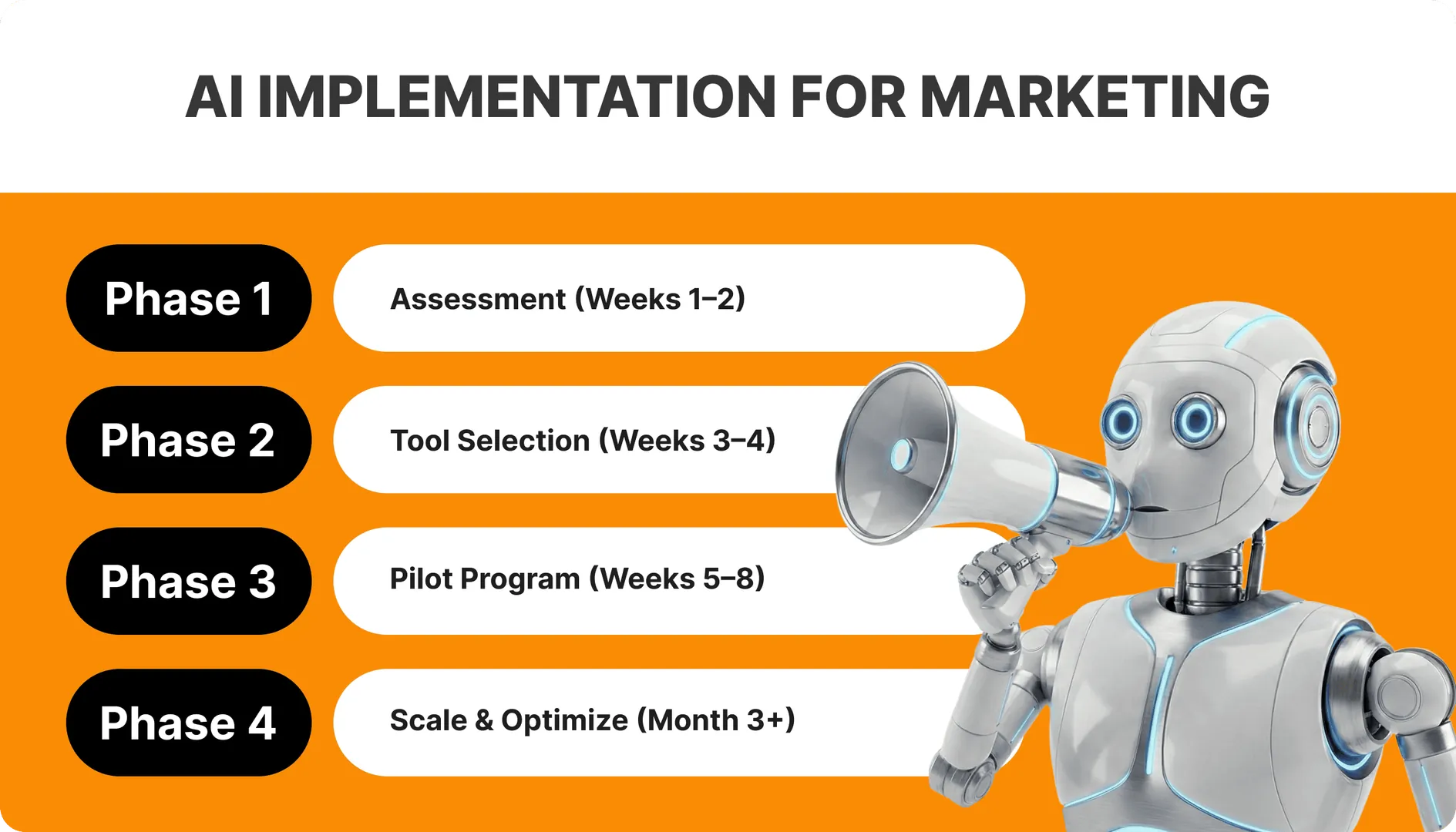
Phase 1: Assessment (Weeks 1–2)
Start with a process audit. Look at content creation, email campaigns, paid ads, social posting, and reporting. Don’t rely on documentation. Talk to the people doing the work. Where do they spend the most time? What tasks feel repetitive or rushed? Where does quality drop when deadlines hit?
Once the work is mapped, identify AI opportunities that are realistic. Early wins usually sit in areas like first drafts of content, headline variations, email subject lines, creative resizing, reporting summaries, or send-time decisions.
Next comes potential ROI. Keep it practical. Estimate hours saved per week, reduction in turnaround time, or expected improvement in engagement. Share findings with marketing leadership, sales (if impacted), and IT if tools touch existing systems.
Assessment checklist
Which tasks repeat weekly or daily?
Where does speed hurt quality?
What work depends heavily on manual effort?
Which teams are most affected?
What would “success” look like in 90 days?
Phase 2: Tool Selection (Weeks 3–4)
Begin by defining requirements based on outcomes, not features. For example: faster blog publishing, better email engagement, or reduced reporting effort. This keeps evaluations focused.
Shortlist the top three tools per category and test them using real work. Avoid demos and sample data. Let the people who will use the tool daily take part in trials. Their feedback on usability often matters more than feature lists.
Compare pricing alongside effort. A cheaper tool that needs constant cleanup can cost more in time than an expensive one that works smoothly. Also check output quality—does it save time or just shift work elsewhere?
Integration checks are critical. If a tool doesn’t connect with your CRM, analytics, or ad platforms, it can create more manual steps. That usually kills adoption.
Decision matrix template
Use-case fit
Ease of use
Output quality
Integration readiness
Cost vs. time saved
The goal is not the “best” tool, but the one that fits the current phase.
Phase 3: Pilot Program (Weeks 5–8)
This phase turns theory into practice. Start with one use case only. Content, email, ads, or reporting but not all at once. Pick the area with the clearest pain point and easiest measurement.
Set KPIs before starting. These might include time saved, volume produced, engagement lift, or cost reduction. Keep metrics simple and visible to the team.
Training should be short and hands-on. Show how the tool fits into existing work instead of forcing new processes immediately. Encourage experimentation, but keep a human review step in place.
As the pilot runs, document workflows. What steps changed? Where does AI help? Where is human input still required? This documentation becomes the foundation for scaling later. Measure results honestly at the end of the pilot. If something didn’t work, call it out and adjust.
Real example
An e-commerce company started with AI-assisted product descriptions. One marketer tested it for four weeks. Output doubled, editing time dropped significantly, and consistency improved. Only after that did they expand the same workflow to category pages and promo emails.
Phase 4: Scale & Optimize (Month 3+)
Expand to additional use cases gradually, building on what already works. For example, move from blog drafts to email copy, then to paid ad variations. Each step should reuse existing learning.
Where helpful, connect tools so work flows naturally content feeding email, email feeding analytics, analytics guiding ads. Avoid over-connecting early; unnecessary complexity slows teams down.
Review performance monthly. Refine prompts, workflows, and review steps. AI output improves as teams learn how to guide it better.
Train additional team members with clear ownership. Not everyone needs full access on day one. Define who creates, who reviews, and who approves.
Over time, internal best practices will emerge. Document them. Share examples. Update playbooks. This is what turns early success into a stable way of working.
Scaling roadmap
Month 3: Expand within the same team
Months 4–5: Add adjacent use cases
Month 6+: Roll out across functions
Measuring AI Marketing Success and ROI
Measuring ROI is the most critical step in validating AI adoption across any function, including marketing. It helps you understand how AI implementation and integration within existing processes deliver better ROI directly or indirectly. Let’s explore this in detail.
ROI Formula
ROI is calculated as:
(Gain from Investment − Cost of Investment) / Cost of Investment
Let’s understand with the quick example:
An organization uses an AI writing tool for blogs, newsletters, and social content.
Manual monthly content cost: $6,000
AI tool subscription: $150/month
AI-generated output equivalent to: $5,000 of manual effort
ROI Calculation:
Gain = $5,000 saved
Cost = $150
ROI = (5,000 – 150) / 150 = 32.3 → 3,233%
AI content tools deliver the fastest and highest return typically within the first month.
If you want to understand which parts of your marketing execution can deliver the highest ROI through AI, you can consult our experts today. Drop us an email at hello.marketricka@gmail.com
Common AI Marketing Mistakes or Challenges to Avoid
Implementing AI in marketing is certainly impressive, but without a proper plan, gaps in adoption can create significant challenges. In this section, we discuss some of the most common yet critical challenges of using AI in marketing.

Mistake #1: Over-automation without human oversight
Automation scales decisions faster than teams expect. When guardrails are unclear, small misjudgments in targeting, messaging, or spend allocation repeat themselves across campaigns before anyone intervenes.
Solution: While integrating AI and even after deployment ensure human-in-the-loop review or intervention by validating AI-driven elements such as targeting and messaging before scaling. Keep escalating human touchpoints whenever AI work has high impact so the system continues to operate within strategic boundaries.
Mistake #2: Impact on AI Performance
AI assumes the provided data is of sufficient quality to be used. When AI is working with outdated or inconsistent data inputs, the result will be a highly accurate but directionally incorrect answer that will ultimately lead to less precision, more inaccurate personalization, inaccurate measurement, and, therefore, reduced effectiveness in optimising.
Solution: Understanding data standards applied consistently across the entire organisation and auditing for quality on a regular basis will help to ensure accurate input to AI systems, as well as having defined ownership for that input. The importance of maintaining quality data should be continuous and not just addressed when a problem occurs.
Mistake #3: Not Training the Team
Teams who are not trained to work with AI outputs either will distrust the AI outputs, or they will accept the outputs without appropriate scrutiny. In both cases, these behaviours will result in diminishing the effectiveness of AI and increasing the risk to a business's operation.
Solution: Training should cover what the output represents (e.g., how to interpret it correctly), and what the specific limitations are, and when it is necessary for human judgement to intervene.
Mistake #4: Expecting Immediate Results
AI systems need time to learn patterns of behaviour and become accustomed to the actual environment and normal operating conditions. At the beginning of the rollout of AI systems, there is typically a lot of volatility in the results, particularly in complex environments.
Solution: Marketers need patience! Set up phased goals, and periodically evaluate the outcomes.
Mistake #5: No strategy when implementing AI
AI implementations can execute activities more effectively but cannot establish the correct or optimal metrics to measure the functionality of these activities. Therefore, it is important for each AI project to have clear metrics to track and evaluate productivity from the start.
Solution: Each AI project must establish a direct alignment to either revenue, cost efficiencies, or customer retention so teams remain on track with the same end result and can quantify the overall success of each AI initiative.
Mistake #6: Privacy and Compliance Issues
The implementation of AI-driven Marketing tools increases the company's exposure to loss due to non-compliance related to its reliance on customer, automated decision-making data.
Solution: Having good governance in place, transparency regarding how data is used, and accountability to internal teams creates trust and helps organizations avoid long-term risks.
Mistake #7: Too Many Tools
Implementing multiple tools at once will create confusion, aisle fragmentation, and significantly slow down adoption.
Solution: Reducing the number of tools you use while integrating fewer, more effective ones will generate better outcomes than relying on a large number of unrelated tools.
The Future of AI Marketing
By 2026 and beyond, AI will become the primary driver of marketing decisions, no longer operating as a secondary system. This shift will happen gradually but will have a significant impact. Marketing teams will spend less time managing tools and more time defining direction, goals, and operational boundaries.
The execution process will be managed by autonomous AI marketing agents who will handle all aspects of their work. The system will execute campaigns while it manages budget changes and creative testing through its ability to react to performance data which it receives during the campaign. Human staff will concentrate on establishing objectives and specifying risk boundaries.
Multi-modal AI will bring coherence to content creation. Text creation and image production plus video development will result from a common understanding between brand identity, messaging content, and performance evaluation requirements. This system reduces team fragmentation while it enables faster development from initial concept to final market-ready product.
Organizations will use real-time personalization as their regular operational method. The system will continuously adapt its messaging based on the real-time signals which it receives from various communication channels. Organizations now must execute disciplined decision-making processes which ensure their personalized content will build trust with customers while maintaining brand identity.
Senior executives will increasingly use AI-centered brand strategy because it now holds business importance. These systems will surface shifts in customer behavior, competitive signals, and market patterns early, helping leaders revisit assumptions before performance declines.
Marketing teams will use their content preparation process to create content before peak periods while they forecast customer demand which will enhance their operational efficiency and productivity.
However, marketing teams will still remain part of the process to ensure everything moves through the right queues. They will need to strengthen their capabilities in data interpretation, AI oversight, and governance.
Are You Ready to Boost Your Marketing Output with AI-driven Processes?
Almost every forward-thinking business and leader is leveraging AI as much as possible—and as responsibly as they can—to accelerate growth and stay ahead of the market. Have you started yet? There is still time to use AI to enhance your marketing productivity, drive innovation, and strengthen strategic roles. You can contact our experts to learn more about how AI is revolutionizing marketing.